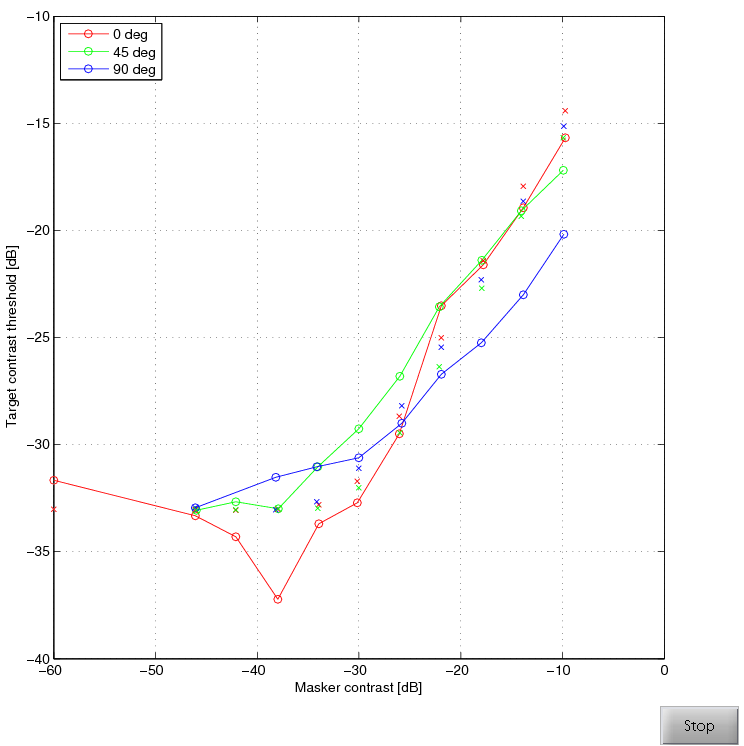
Metric fitting results
Metric "HDR-VDP-2.0"Test set "Foley's masking data"
R = 2 dB
See the gallery of stimuli.
About the data set "Foley's masking data"
Recreated stimuli from Foley's masking measurements
The data set recreates the stimuli used for the contrast masking
measurements described in:
John M. Foley, "Human luminance pattern-vision mechanisms: masking
experiments require a new model," J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 11, 1710-1719
(1994). link. The
detection thresholds were read from Figure 3b, data for KMF. Stimuli
dimensions have been changed so that all images are square and
cyclic.
The stimuli contain the detection thresholds for a Gabor patch in
the presence of a masking signal. The masking signal has the same
frequency as the Gabor patch. The orientation of the masking signals
is 0 deg (the same orientations as the Gabor), 45 deg or 90 deg.
About the metric "HDR-VDP-2.0"
This is the proposed metric described in
detail in the paper "HDR-VDP-2: A calibrated visual metric for
visibility and quality predictions in all luminance conditions" (doi). It shares
many similarities with VDP'93 and HDR-VDP, as it was inspired by these
metrics, but the functionality is much extended and individual
components are thoroughly revised. The major differences are:
- The metric predicts both visibility (detection/decrimination)
and image quality (mean-opinion-score).
- The metric is based on new CSF measurements, made in the
consistent viewing conditions for a large range of luminance and
frequency.
- The new metric models L-, M-, S- and rod sensitivities and is
sensitive to different spectral characteristic of the incoming
light.
- Photoreceptor light sensitivity is modelled separately for cones
and rods, though L and M cones share the same characteristic.
- The intra-ocular light scatter function (glare) has been fitted
to the experimental data.
- The model used a steerable pyramid rather than cortex transform
to decompose image into spatially- and orientation-selective
bands. Steerable filter introduces less ringing and in general case
is computationally more efficient.
- The new model of contrast masking introduces inter-band masking
and the effect of CSF flattening.
- A simple spatial-integration formula using probability summation
is used to account for the effect of stimuli size.
